How the datacenters are built. How the cloud runs. Where the world is going.
09 May 2018
Reading time ~13 minutes
Since there is no material on ICT Infastructure course, I’m trying to recap all lessons done in this page. The notes are written trying to remember the contents of the course (in accordance with the OneNote Notebook published on course page) and then expanding that contents with structured resources found online. If you find any error please, fork and push!
Introduction
The world is changing and a lot of axiom are becaming false. Some example? In the bechelor course (and not, sigh), the teachers say: “The main bottleneck is the disk”, and so all the performance are evalueted with reference to disk usage, number of IOs operations and so on… This, nowadays, is false. Just thing of Intel Optane SSD where the new SSD tecnologie based on 3D NAND permits to write and read more fast then previous SSD (the disk that we have installed on our system, sigh number 2), and so we have to redesign the system. Some distributed file system, written in ’90s, are crashing due the axiom that the disks are slower than CPU and so you have enough time to do all the computation needed. False!
Anothe example is in application and server distribution. In the past many application was managed on each server with a shared storage, nowadays we have deploy a large application on a custers of server with local storage, so new system to develop and manage distributed computing application is needed (Hadoop, cassandra (distributed DB), Spark (Computation)…).
The world is evolving faster than I can write this notes, so maybe some things written here are already obsolete, so we can not waste any more time on introduction to avoid to need to rewrite the introduction.
Let’s start to see how a datacenter is build to support new requests.
Fabric
The fabric is the interconnection of node in a datacenter. We can think this level as a bunch of switch and wires.
Ethernet
The connection can be performed with various technologies, the most famous is Ethernet, commonly used in Local Area Networks (LAN) and Wide Area Networks (WAN). Ethernet use twisted pair and fiber optic links. Ethernet as some famous features such as 48-bit MAC address and Ethernet frame format that influenced other networking protocols.
Infiniband
Even if Ethernet is so famous, there are other standard to communicate. InfiniBand (IB) is another standard used in high-performance computing (HPC) that features very high throughtput and very low latency. InfiniBand is a protocol and a physical infrastructure and it can send up to 2GB massages with 16 priorities level. The RFC 4391 specifies a method for encapsulating and transmitting IPv4/IPv6 and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) packets over InfiniBand (IB).
InfiniBand trasmits data in packets up to 4KB. A massage can be:
- a direct memory access read from or write to a remote node (RDMA)
- a channel send or receive
- a transaction-based operation (that can be reversed)
- a multicast trasmission
- an atomic operation
Omni-Path
Moreover, another communication architecture that exist and is interested to see is Omni-Path. This architecture is owned by Intel and performs high-performance communication. Production of Omni-Path products started in 2015 and a mass delivery of these products started in the first quarted of 2016 (you can insert here some more stuff written on Wikipedia). The interest of this architecture is that Intel plans to develop technologiy based on that will serve as the on-ramp to exascale computing (a computing system capacle of the least one exaFLOPS).
RDMA
If you read wikipedia pages about IB and OmniPath you will find a acronym: RDMA. This acronym means Remote Direct Memory Access, a direct memory access (really!) from one computer into that of another without involving either one’s OS, this permits high-throuhput, low-latency networking performing.
Some consideration about numbers
Start think about real world. We have some server with 1 Gbps (not so high speed, just think that is the speed you can reach with your laptop attaching a cable that is in classroom in the univesity). We have to connects this servers to each other, using a switches (each of them has 48 ports). We have a lots of servers… The computation is done.

Real use case
As we see we need a lots of bandwith to manage a lots of service (you don’t say?) and even if the north-south traffic (the traffic that goes outsite from our datacenter) can be relatively small (the university connection exits on the world with 40 Gbps), the east-west traffic (the traffic inside the datacenter) can reach a very huge number of Gbps. Aruba datacenter (called IT1) with another Aruba datacenter (IT2) reach a bandwidth of 82 Gbps of Internet connection.
Yesterday I went to master degree thesis discussion of my friend. He is a physicist and his experiment requires 2.2Tbps of bandwidth to store produced data, so public cloud is impossible to use. How can manage 2.2 Tbps? Maybe we can reply to this answer (hopefully, otherwise the exam is failed :/ ).
Connectors
Now we try to analyse the problem from the connector point of view. The fastest wire technology avaiable is the optic fiber. It can be divided into two categories: monomodal (1250 nm) or multimodal (850 nm). Of course, the wire is a wire, and we need something to connect it to somewhere. One of them is the Small form-factor pluggable transceiver (SFP), a compact, hot-pluggable optical module transceiver. The upgrade of this connector is the SFP+ that supports data rates up to 16 Gbps. It supports 10 Gigabit ethernet and can be combined with some other SFP+ with QSFP to reach 4x10Gbps. If combined with QSFP28 we can reach 100 Gbps on the ethernet that is the upper limit nowadays for the data rate.
Software Defined __
The Software Defined something, where something is Networking (SDN) or Storage (SDS), is a novel approch to cloud computing.
SDN
SDN is an architecture purpoting to be dynamic, manageable, cost-effective and some more nice attribute readable here. This type of software create a virtual network to manage the network with more simplicity.
The main concept are the following:
- Network control is directly programmable
- The infrastructure is agile, since it can be dynamically adjustable
- It is programmatically configured and is managed by managed by a software-based SDN controller
- It is Open Standard-based and Vendor-neutral
SDS
Software-defined Storage is a term fro computer data storage software for policy-based provisioning and management of data storage independent of the underlying hardware. This type of software includes a storage virtualization to separate storage hardware from the software that manages it.
Software-defined data center
Software-defined data center is a sort of upgrade of the previous term and indicate a series of virtualization concepts such as abstraction, pooling and automation to all data center resources and services to achieve IT as a service.
Hyperconvergence
So we virtualize the networking, the storage, the data center… and the cloud! Some tools, as Nutanix build the hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) technology.
Network topologies
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
The spanning Tree Protocol is a network protocol that builds a logical loop-free topology for Ethernet networks. The spanning tree is built using some Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) frames. In 2001 the IEEE introduced Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) that provides significantly faster spanning tree convergence after a topology change. Why so useful?
Three-tier design
This architecture is simple architecture where each component has a redundant unit to replace it in case of failure.
Spine and leaf Architecture
With the increased focus on east-west data transfer the three-tier design architecture is being replaced with Spine-Leaf design. The switches are diveded into 2 groups, the leaf switches and spine switches. Every leaf switch in a leaf-spine architecture connects to every switch in the network fabric. In that topoligy the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) is used. It provides a method to control the bundling of several physical ports together to form a single logical channel.
Full Fat Tree
In this network topology, the link that are nearer the top of the hierarchy are “fatter” (thicker) than the link further down the hierarchy. 
VLAN
Now, the problem is that every switch can be connected to each other and so there is no more LANs separation in the datacenter, every packet can go wherever it wants and some problems may appear. For this problem the VLAN is invented. It partition a broadcast domain and create a isolated computer network.
It works by applying tags to network packets (in Ethernet frame) and handling these tags in the networking systems. 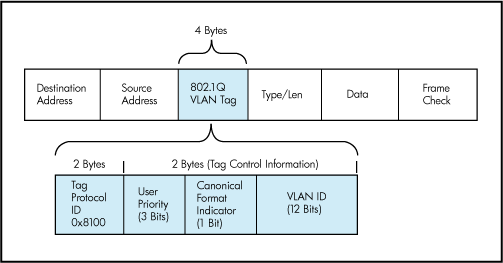
A switch can be configured to accept some tags on some ports and some other tags on some other ports.
VLAN are useful to manage the access control to some resources (and avoid to access to some subnetwork from other subnetwork).
Switch Anatomy
A switch is an ASIC (application-specific integrated circuit). It can be proprietary architecture or non-proprietary.
It can be see as two plane that cooperate, the control plane and the data plane. The first runs an OS (Linux, BSD…) and expose a CLI to configure it. The second plana manges the data.
Now some standard are trying to impose a common structure to the network elements (switch included) to facilitate the creation of standard ochestration and automation tools. 
Storage
After the fabric, another fondamental component of a datacenter is the storage. The storage can be provided with various tecnologies. The simple one is that the disk are put inside each servers and are used as we use the disk on our laptop. Of course it is not useful is we have a bunch of data to manage, and some networking solution can be better to use.
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
NAS is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. NAS systems are networked appliances which contain one or more storage drives, often arranged into logical, redundant storage containers or RAID. They typically provide access to files using network file sharing protocols such as NFS, SMB/CIFS, or AFP.
Storage Area Network (SAN)
While NAS provides both storage and a file system, SAN provides only block-based storage and leaves file system concerns on the “client” side. SAN protocols include Fibre Channel, iSCSI, ATA over Ethernet (AoE) and HyperSCSI.
Benefits
The main features that are provided by a storage system are the following:
- Thin provisioning
- This is a virtualization technology that gives the appearance of having more physical resources than are actually avaiable. Thin provisioning allows space to be easily allocated to servers, on a just-enough and just-in-time basis. Thin provisioning is called “sparse volumes” in some contexts.
- Deduplication
- If the same file is required in two context, it is saved one time and is served to different context.
- Compression
- Authentication
- RTO/RPO “support” DR - The Recovery Point Objective is defined by business continuity planning. It is the maximum targeted period in which data might be lost from an IT service due to a major incident.
- Network Interface (iSCSI, Fibre Channel…)
- RAID
- Tiering - Tiering is a technology to assign a category to data to choose various type of storage media to recude total storage cost. Tiered storage policies place the most frequently accessed data on the highest performing storage. Rarely accessed data goes on low-performance, cheaper storage.
- NAS Protocols
- Snapshot
Non-RAID drive architectures
Also other architectures exist and are used when RAID is too expensive or not required.
- JBOD (“just a bunch of disks”): multiple hard disk drives operated as individual independent hard disk drives
- SPAN: A method of combining the free space on multiple hard disk drives from “JBoD” to create a spanned volume
- DAS (Direct-attached storage): a digital storage directly attached to the computer accessing it.
Some consideration about Flash Drives
The bottleneck in new drives is the connector. The SATA connector is too slow to use SSD at the maximum speed. Some results can be see here.
The solution? Delete the connector and attach it to PCIe. So new Specification is used, the NVMe, an open logical device interface specification for accessing non-volatile storage media attached via a PCI Express bus.
Storage in the feature

As we can see in the image, it’s been decades since the last mainstream memory update is done. In fact, the SSD became popular in the last years due the cost but they exists since 1989.

New technology was introduced in 2015, the 3D XPoint. This improvement takes ICT world in a new phase? If yesterday our problem was the disk latancy, so we design all algorithm to reduce IOs operation, now the disk is almast fast as the DRAM, as shown the following image:
With the NVMe drives we can reach 11GBps, aka 88 Gbps. Since the software latency is circa 5 microseconds, TCP/IP software introduces also a latency, 70-80 microseconds, the disk is no more a problem.
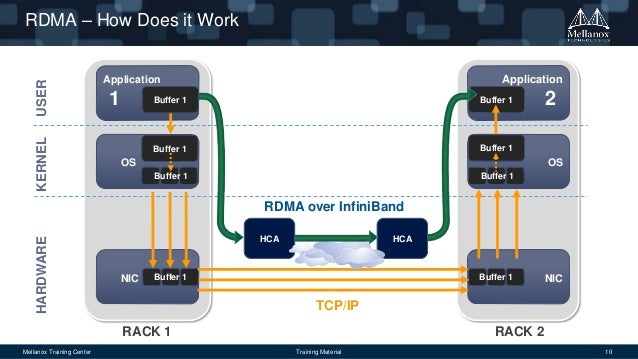
Hypervisors
A hypervisor is a software, firmware or hardware that create and runs virtual machines. It can be bare-metal hypervisor or hosted hypervisor. A bare-metal is where the hypervisor is the OS itself, often requires certified hardware. Hosted hypervisor is VirtualBox.
An hypervisor permits to overbook physical resources to allocate more resources than exist.
It create also a virtual switch to distribute the networking over all VMs.
Cloud
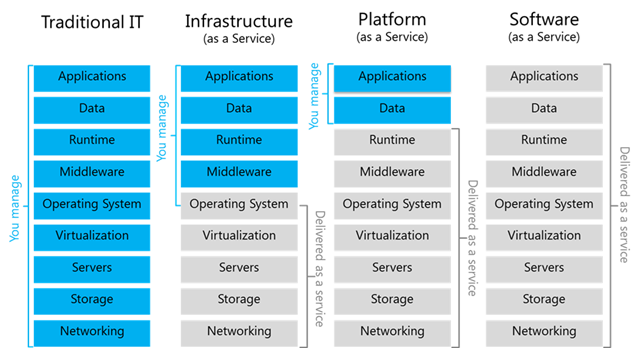
The cloud is someone else’s computer that you can use to execute your application with more realiable feature than your laptop. A cloud is a collection of network-accessible IT resources.
Rapid Elasticity
Consumers can adapt to variation in workloads and mantain required performance levels. This permits also to reduce costs avoiding the overprovisining.
High Avaialability
The cloud provide high avaialabity. This feature can be achived with redundancy of resources to avoid system failure. Some Load Balancer is used to balance the request between all the resources to avoid failure due the resources saturation on some machine.
The cloud infrastrucure can be public, if is provisioned for open use by the general public, or private, if is provisioned for exclusive use by a single organization comprising multiple consumers.
Cloud computering Layer
The cloud infrastrucure can be see as a layered infrastructure.
Phyisical Layer
Executes requests generated by virtualization and control layer. Specifies entities that operate at this layer (devices, systems, protocols…)
Virtual Layer
Deployed on the physical layer. Abstract physical resources and makes them appear as virtual resources. Executes the requests generated by control layer.
Control Layer
Enables resource configutarion and resource pool configuration. Enable resource provisioning. Execute requests generated by service layer.
Service orchestration Layer
Provides workflow for executing automated tasks
Security
Firewall, Antivirus, Standard procedures to direct safe execution of operations…
Vendor Lock-in
The cloud introduces some problems, one of them is the vendor lock-in. It appers when I write a software that uses a vendor API that not respects any standard. If I would like to change cloud I use, I need to modify the code (good luck!).
Orchestration
Fog Computing
The fog computing is an architecture that uses one or more collaborative end-user clients or near-user edge devices to carry out a substantial amount of storage (rather than stored primarily in cloud data centers), communication (rather than routed over the internet backbone), control, configuration, measurement and management (rather than controlled primarily by network gateways such as those in the LTE core network).
References
- https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4391
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Omni-Path
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Remote_direct_memory_access
- https://www.arubacloud.com/infrastructures/italy-dc-it1.aspx
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software-defined_networking
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software-defined_storage
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software-defined_data_center
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spanning_Tree_Protocol#Rapid_Spanning_Tree_Protocol
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multitier_architecture
- https://blog.westmonroepartners.com/a-beginners-guide-to-understanding-the-leaf-spine-network-topology/
- http://searchdatacenter.techtarget.com/definition/Leaf-spine
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network-attached_storage
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Non-RAID_drive_architectures
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fog_computing
- https://www.openfogconsortium.org
